0x2306 - Forced alignment method
Index | Sub Index | Name | Data Type | Acc. | Pdo Map. | NVM | Value range | Default value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x2306 | 0x01 | Process time | UINT32 | RW | No | Yes | UINT32 | 1000 | milliseconds |
0x2306 | 0x02 | Process current | UINT32 | RW | No | Yes | UINT32 | 500 | ‰ rated current |
0x2306 | 0x03 | Process tolerance | UINT8 | RW | No | Yes | UINT8 | 5 | % |
| 0x2306 | 0x04 | Motor is phased | UINT8 | RW | No | No | 0 or 1 | 0 | - |
0x2306 | 0x05 | Alignment procedure type | UINT8 | RW | No | Yes | 0 or 1 | 0 | - |
0x2306 | 0x06 | Shaking time | UINT16 | RW | No | Yes | UINT16 | 200 | ms |
0x2306 | 0x07 | Shaking max voltage | UINT16 | RW | No | Yes | 0 to 1000 | 30 | ‰ Vbus |
0x2306 | 0x08 | Shaking frequency | UINT16 | RW | No | Yes | UINT16 | 15000 | mHz |
0x2306 | 0x09 | Minimum angle variation | UINT16 | RW | No | Yes | UINT16 | 300 | increments |
This object provides access to Forced alignment method parameters which is one of the possible methods for the initial angle determination process.
SubIndex description:
- 0x01 (Process time): This object determines the duration in milliseconds of the whole process (alignment between two phases). If the process is repeated it will use this time for each repetition.
- 0x02 (Process current): This object determines the current used by the process.
- 0x03 (Process tolerance): This object determines the maximum tolerated error in process around the expected displacement. The value is expressed as a percentage of the expected displacement.
- 0x04 (Motor is phased): This object allow to know if 'forced alignment' has been performed with the active configuration, this register will show a '0' when the phasing has not been performed, and '1' when the motor is phased. A trigger of 'forced alignment' process can be performed by writing a 0 in this sub-index.
0x05 (Alignment procedure type)
Value
Alignment type selection
0 Classic forced alignment 1 Shaking forced alignment - 0x06 (Shaking time): Time for take vibration measures. This is not an absolute time, if the vibration generated during this period does not produce the desired minimum angle variation (subindex 0x9), the drive will repeat the process with applying a larger amount of current to the motor (with a maximum of 6 attempts).
- 0x07 (Shaking max voltage): This register modifies the maximum voltage applied in shaking stage. At shaking stage the motor will begin applying 1/6 of the indicated voltage, and will be progressively increased until reach This maximum value. Bigger values implies a larger vibration amplitude.
- 0x08 (Shaking frequency): This register modifies the injected signal frequency to induce vibration.
- 0x09 (Minimum angle variation): Minimum angle variation to validate angle measurements, also to ensure that feedback is working (in UINT16 angle units).
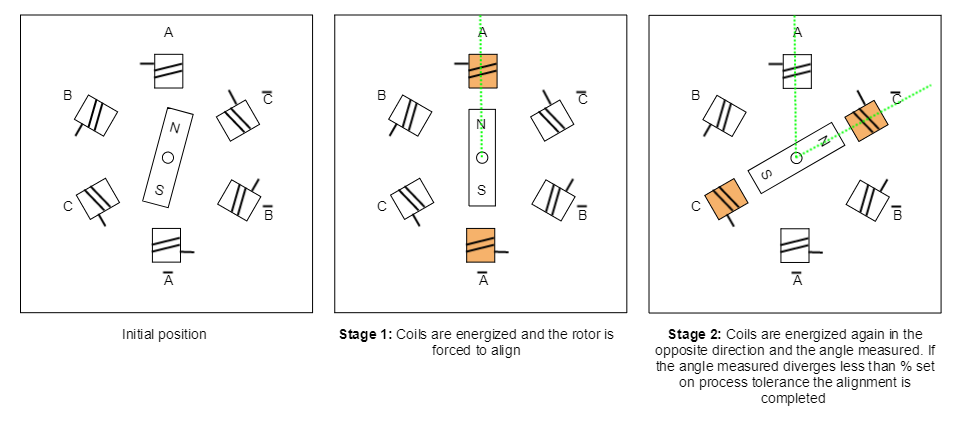
Classic Forced Alignment
This method forces the rotor to align in the direction of two different phases and check if the angular increment measured using commutation sensor match the expected one. If this condition is not satisfied the process is repeated changing the used phases until it completes all possibilities.
Registers used in classic alignment method: subindexes 0x01, 0x02, 0x03 and 0x04
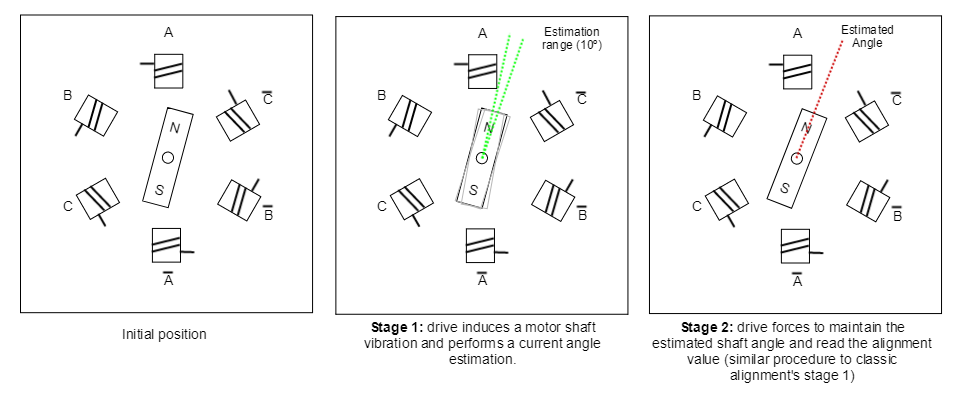
Shaking Forced Alignment
This method allows to detect the motor position in electrical angle terms by means of vibration. First the drive forces to vibrate the motor and performs an electrical angle estimation, this estimation has a tolerance of ±10 degrees approximatelly (it can variate depending on the motor design).After the actual angle is found, the drive forces the motor to go to this angle and then performs the phasing with this reading. This second stage of the alignment allows to increase the commutation precision to 1 or 2 degrees instead of the previous estimated tolerance.
After forcing the estimated shaft angle, the drive does not perform any alignment check (unlike classic alignment). The unique verification that this method performs is in the vibration stage, the drive forces the vibration with different amplitudes (increased progresivelly), if the vibration is not detected after several attepmts will throw a fault. This can be produced by two possible causes: the first possible cause is that the feedback is not connected (or configured) properly or the resolution is too low, the second cause can be that 0x09 (minimum angle variation) value is too high and/or 0x07 (Shaking max voltage) value is too low.
Pros and cons
+ Reduced movement of motor shaft in phasing procedure, motor will tend to vibrate instead of moving like classic alignment.
+ It is possible to reduce the total alignment duration time without losing precision.
+ Better for linear motors.
- Is quite more difficult to configure than classic alignment.
- Alignment is not checked after phasing as classic does.
Registers used in shaking alignment method: Subindexes 0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, and 0x09.
Note that subindex 0x03 is not used in this method.